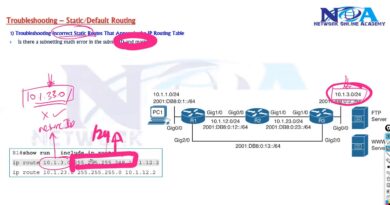
IP Address Bite Size Learning
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique identifier assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It is used to identify and communicate with other devices on the network.
An IP address is a numerical address that consists of a series of four numbers separated by dots, such as 192.168.1.1. The numbers in an IP address can range from 0 to 255, and the four numbers together form a 32-bit address that can represent over four billion unique addresses.
There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 addresses use a 32-bit format and are the most commonly used type of IP address, but due to the limited number of unique addresses available, IPv6 addresses were developed. IPv6 addresses use a 128-bit format and can represent a much larger number of unique addresses than IPv4.
IP addresses are used by network protocols to route data packets between devices on a network. Each device on a network has a unique IP address, which allows it to be identified and communicate with other devices on the network. IP addresses can be assigned manually, such as by a network administrator, or automatically, such as through the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) used by most home and business networks.
ipv4