IP ADDRESSING PART 3 | CLASS OF IP ADDRESS | APIPA | ALTERNATE CONFIGURATION |
IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numbers that are typically displayed in dotted decimal notation. A 32-bit address contains two primary parts: the network prefix and the host number.
All hosts within a single network share the same network address. Each host also has an address that uniquely identifies it. Depending on the scope of the network and the type of device, the address is either globally or locally unique. Devices that are visible to users outside the network (webservers, for example) must have a globally unique IP address. Devices that are visible only within the network must have locally unique IP addresses.
IP addresses are assigned by a central numbering authority known as the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). IANA ensures that addresses are globally unique where needed and has a large address space reserved for use by devices not visible outside their own networks.
ip address
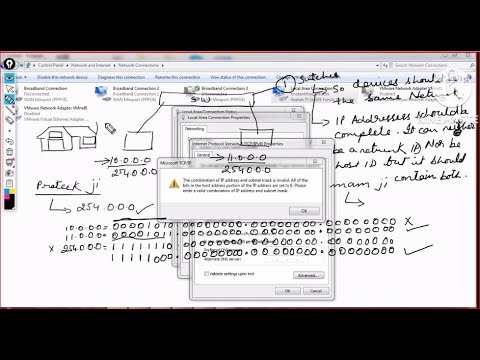

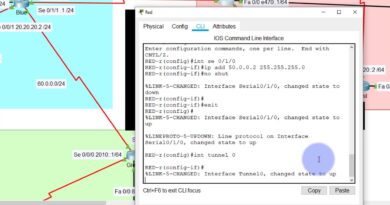

nice content
Nicely explained
Well explained