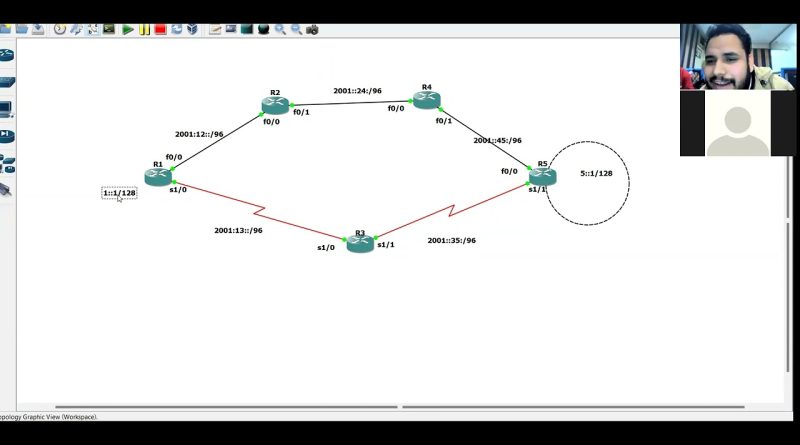
RIP Next Generation protocol| Doubt class | RipNg Part-2 | Ipv6 Ripng configuration | Network Zeal
RIPng is a distance-vector routing protocol used for routing IPv6 traffic. While RIPng has been a useful protocol in some networking scenarios, it has limitations and is not as widely used as other routing protocols like OSPFv3 and BGP for IPv6 networks.
@RajeevPrashar #IPv6 #RIPNG
The statement “RIPng IPv6” could mean different things depending on the context:
1. RIPng is no longer used: If you mean that RIPng is no longer a popular or recommended routing protocol for IPv6 networks, that statement is generally true. Network administrators often prefer OSPFv3 or BGP for more advanced and scalable IPv6 routing.
2. RIPng protocol updates: RIPng, like other networking protocols, may have received updates or improvements over time. It’s possible that there have been changes or enhancements to the RIPng protocol itself.
3. RIPng being phased out: If you mean that RIPng is being phased out or deprecated, it’s essential to note that network protocols can continue to exist and be used in specific scenarios even if they are less commonly deployed.
The choice of a routing protocol for an IPv6 network depends on various factors, including the network’s size, complexity, and specific requirements. Network administrators should select the routing protocol that best suits their needs, considering factors such as scalability, stability, and security.
RIPng (Routing Information Protocol Next Generation) is an extension of the original RIP (Routing Information Protocol) designed for IPv6, the next-generation Internet Protocol. IPv6 was developed to address the limitations of IPv4, which include address space exhaustion and a lack of support for modern networking requirements.
RIPng operates similarly to its predecessor, RIP, but it is adapted to work with IPv6 networks. Some key features and characteristics of RIPng include:
1. IPv6 Compatibility: RIPng is specifically designed to work with IPv6 addresses, which are 128-bit in length compared to the 32-bit addresses used in IPv4.
2. Hop Count Metric: Like RIP, RIPng uses hop count as its routing metric. Each router in the network increments the hop count when it forwards a packet, and RIPng routers exchange routing information to calculate the best path to reach a destination.
3. Distance Vector Protocol: RIPng is a distance vector routing protocol, which means that routers periodically exchange routing tables to update their knowledge of the network topology. RIPng routers send updates every 30 seconds by default.
4. Maximum Hop Count: RIPng has a maximum hop count limit of 15 hops. If a route exceeds this limit, it is considered unreachable.
5. Split Horizon: RIPng includes a split horizon mechanism to prevent routing loops. Routers do not advertise routes back to the same interface from which they were learned.
6. Route Tagging: RIPng supports route tagging, allowing routers to add additional information to routes. This can be useful for policy-based routing.
7. Route Authentication: Like RIP, RIPng can use simple authentication mechanisms to ensure the integrity of routing updates.
While RIPng is a simple and easy-to-configure routing protocol, it has limitations, such as slow convergence and a lack of support for more advanced features found in other routing protocols like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol). As a result, RIPng is typically used in small to medium-sized networks with relatively simple topologies where faster convergence and more advanced features are not critical. In larger or more complex networks, other routing protocols are often preferred.
ipv4
-390x205.jpg)
🤩🤩🤩🤩🤩
sir your style is unique
Nice to see you sir ..Please make your videos with Face