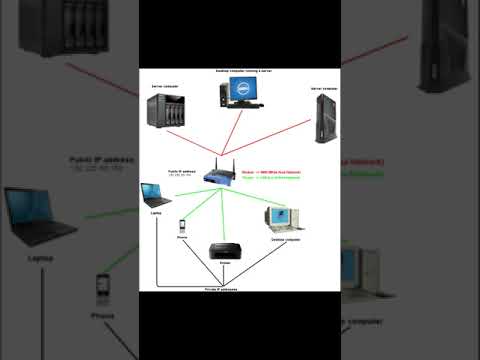
What is IP address?
An Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing.
IP addresses are a unique series of numbers that are used to identify devices on the internet. They can be compared to a mailing address, but instead of identifying a physical location, they identify a network device. IP addresses are essential for the internet to work, as they allow devices to communicate with each other.
There are two main versions of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 addresses are made up of four numbers, each between 0 and 255, separated by periods. For example, 192.168.1.1 is a valid IPv4 address. IPv6 addresses are made up of eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons. For example, 2620:0:1cfe:face:b00c:0:2e0:1 is a valid IPv6 address.
IP addresses can be either static or dynamic. A static IP address is assigned to a device permanently, while a dynamic IP address is assigned to a device temporarily. Most devices on the internet have dynamic IP addresses, which are assigned by their internet service provider (ISP).
IP addresses are used for a variety of purposes, including:
Routing traffic: When you visit a website, your computer sends a request to the website’s IP address. The website’s server then sends the website’s content back to your computer’s IP address.
Security: IP addresses can be used to block access to certain websites or services. For example, a school might block access to social media websites using their IP addresses.
Location tracking: IP addresses can be used to track the approximate location of a device. This is often used to provide location-based services, such as weather forecasts or maps.
It is important to note that IP addresses are not always accurate. For example, if you are using a VPN, your IP address will be different from your actual IP address. Additionally, some websites and services may use IP geolocation databases to estimate your location, but these databases are not always accurate.
ipv4